Inoculation, culture, isolation, purification, identification and preservation of microorganisms
Inoculation
The process of attaching a microorganism to an artificial medium or to a living organism suitable for its growth and propagation is called inoculation.
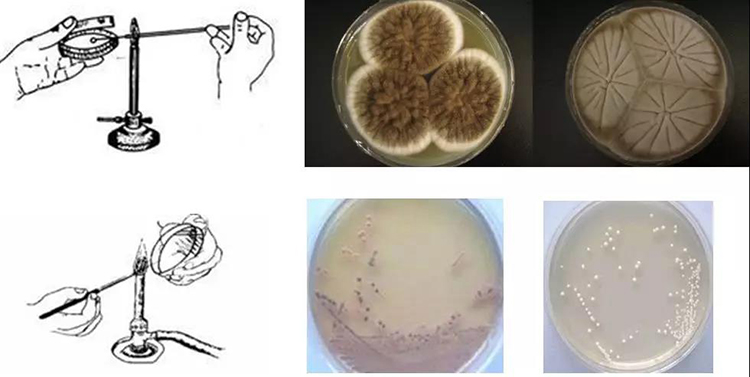
Inoculation and separation tools
1. Inoculating needle 2. Inoculating ring 3. Inoculation hoe 7. Small scalpel
The commonly used methods of inoculation are as follows:
1. Line inoculation
This is the most common method of inoculation. That is, by moving the solid medium surface back and forth in a straight line, the effect of inoculation can be achieved. The commonly used inoculation tools are vaccination ring, vaccination needle, etc. This method is commonly used in inclined plane inoculation and plate marking.
2. Inoculation at three o ‘clock
This method is often used in the study of mold morphology. This method is to inoculate a small amount of microorganisms on the surface of the plate, forming three points of an equilateral triangle, and let them form colonies independently, and then observe and study their morphology. In addition to the three points, there are also a little or more vaccination.
3. Puncture inoculation
This method is often used to preserve anaerobes or to study the dynamics of microorganisms. In the case of puncture inoculation, the inoculation tool used is a needle. The medium used is usually semisolid. It is done by dipping a small number of bacteria with a needle and puncturing them in a straight line from the center of the semi-solid medium to the bottom of the tube. If a bacterium has flagella and can move, it can grow around the puncture line.
4. Pouring and mixing inoculation
The method is to put the microorganisms to be accepted into a petri dish, and then pour into a solid medium cooled to about 45° C, quickly and gently shake well, so that the bacteria liquid to achieve the purpose of dilution. After the plates have solidified and are incubated at the right temperature, individual microbial colonies can grow.
5. coating inoculation
It is slightly different from pouring and mixing inoculation, that is, first pour the plate, let it solidify, and then pour the bacteria liquid into the plate, quickly use the coating rod to coat the surface back and forth, so that the bacteria liquid is evenly distributed, and a single microbial colony can grow.
6. Liquid inoculation
Liquid inoculation may be the washing of bacteria from a solid culture medium into a liquid culture medium, or the pipetting of bacteria from a liquid culture to a liquid culture medium, or the removal of bacteria from a liquid culture to a solid culture medium.
7. Inoculation
This method is to use the method of injection to transfer the microbe to be connected to a living organism, such as people or other animals, the common vaccine vaccination, is to be injected into the human body, to prevent certain diseases.
8. Live inoculation
In vivo inoculation is a method used specifically to grow viruses or other pathogenic microorganisms because viruses must be inoculated in living organisms to grow and reproduce. The living body can be the whole animal; It can also be an isolated living tissue, such as a monkey kidney. It can also be a developing chicken embryo. The way of inoculation is injection, can also be mixed feeding.
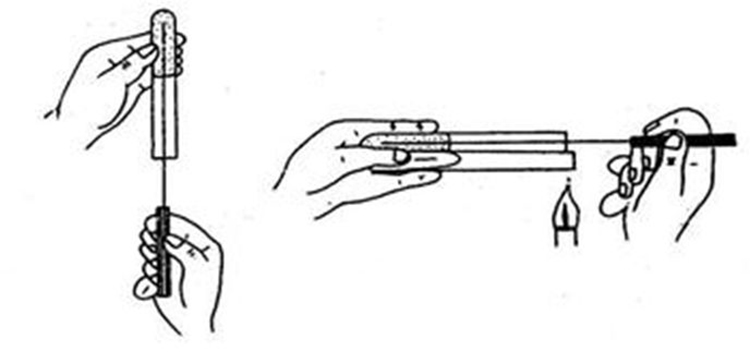
Note: All inoculations must be performed aseptically
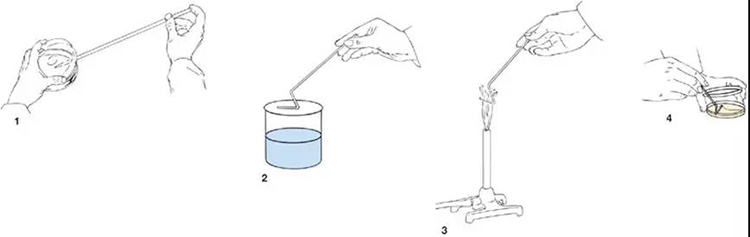
After the medium is autoclaved, sterilized tools (such as needles and pipettes, etc.) are used to inoculated the bacteria-containing materials (such as samples, moss or bacterial suspension, etc.) on the medium under sterile conditions. This process is called aseptic inoculation operation. All inoculations in laboratory tests must be performed aseptically.
(1) Inoculation and sterilization
(2) Open the tampon plug
(3) Sterilization of tube orifice
(4) Stir the mosses
(5) Inoculation
(6) Put the cotton plug well.
Separation and purification
Cultures that contain more than one kind of microorganism are called mixed cultures. If all the cells in a colony come from one parent, the colony is called a pureculture. In the identification of bacteria, the microorganisms used are generally required to be pure cultures. The process by which pure culture is obtained is called separation and purification, and there are many methods.
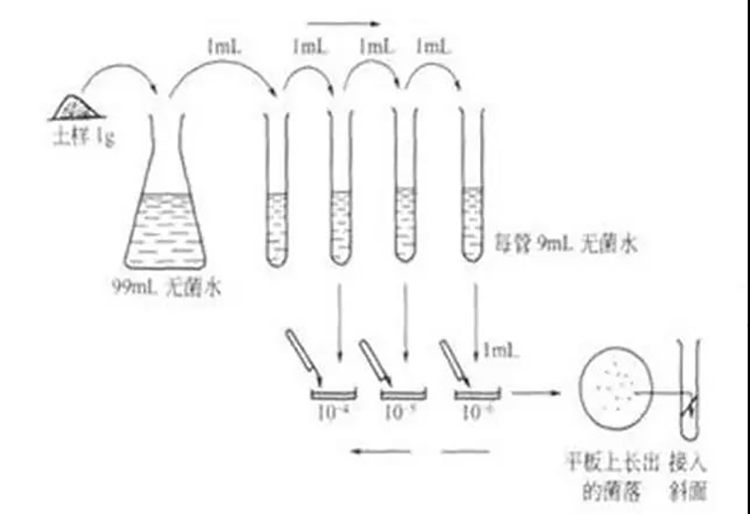
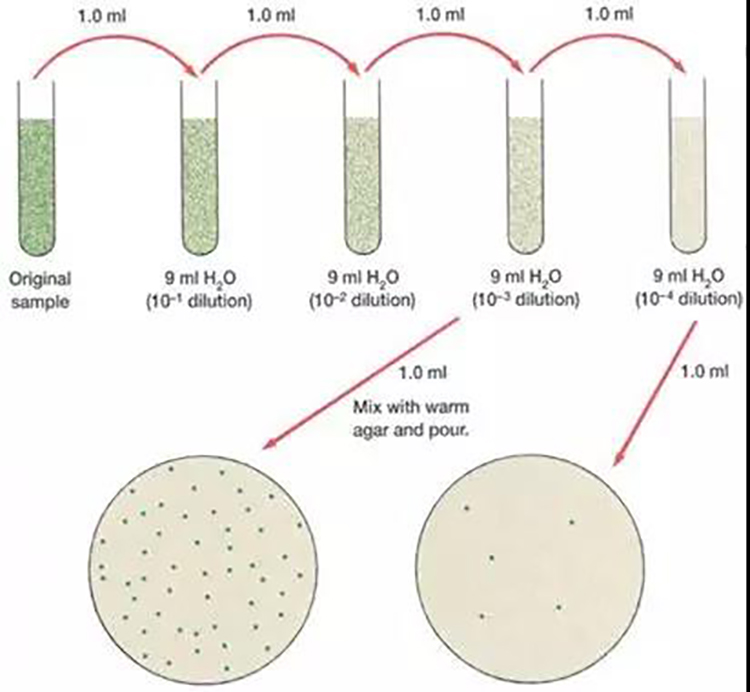
1.Pour plate method
The microbial suspension was first diluted through a series of dilutions, a certain amount of which was fully mixed with a melted nutrient AGAR medium maintained at about 40-50°. This mixture was then poured into a sterile petri dish, which, after solidification, was placed upturned in a constant chamber. After multiple proliferation of a single cell, a colony is formed. A single colony is taken to make a suspension, and the above steps are repeated several times to obtain a pure culture.
2. Coating plate method
Firstly, the microbial suspension was diluted appropriately, a certain amount of diluent was put on the sterile and solidified nutrient AGAR plate, and then the diluent was evenly coated on the surface of the medium with a sterile glass scraper, and a single colony could be obtained after constant temperature culture.
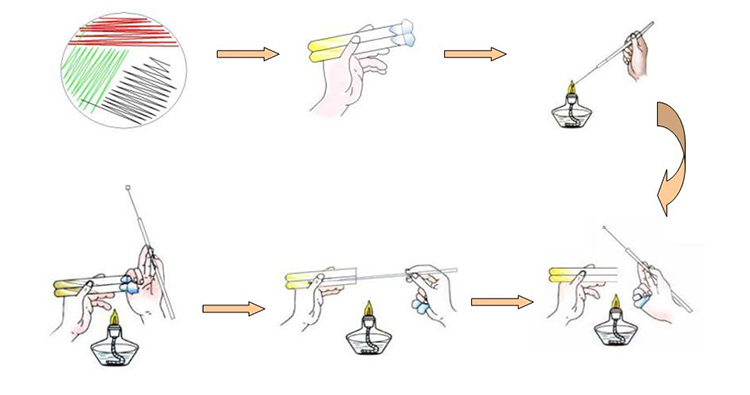
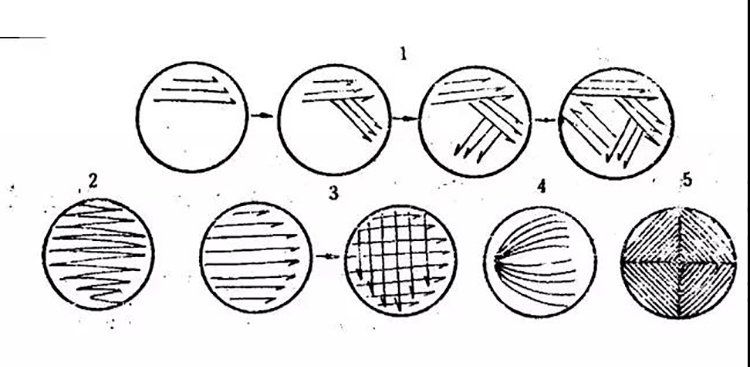
3.Plate marking method
The simplest method of microbial isolation is the plate scribing method. Use a sterile inoculation ring to take a little of the culture and line it on a plate. There are many methods of scribing, and the common scribing methods that are easy to appear a single colony are oblique line method, curve method, square method, radiation method, four grid method, etc. As the ring moves backward on the surface of the culture medium, the bacterial fluid on the ring is gradually diluted until individual cells are scattered on the line, and each cell grows into a colony after culture.
4. Enrichment culture method
The method and principle of enrichment culture are very simple. We can create conditions in which only the desired microbes can grow, and under these conditions, the desired microbes can effectively compete with other microbes and far outgrow them in terms of their ability to grow. If some obligate parasites are to be isolated, the sample must be inoculated into the corresponding population of sensitive host cells and allowed to grow in large numbers. Pure parasites can be obtained by repeated transplantations.
5.Anaerobic method
In the laboratory, to isolate certain anaerobic bacteria, a tube containing the original culture medium can be used as a culture vessel. The tube is heated in a boiling water bath for several minutes to expel the dissolved oxygen from the culture medium. It is then quickly cooled and inoculated. After inoculation, sterile paraffin wax was added to the surface of the medium to insulate the medium from air. Another method is to replace the gas in the medium with N2 or CO2 after inoculation, and then seal the opening of the tube over the flame. Sometimes in order to isolate some anaerobic bacteria more effectively, the isolated sample can be inoculated on the medium, and then the dish is placed in a completely sealed anaerobic culture device.
6.Single cell (or single spore) separation method
Pure culture is obtained by directly separating individual cells or individuals from a mixed population by microscopic separation. For larger microorganisms, individual extractions can be made using capillary tubes. For relatively small microorganisms, a micromanipulator is used to pick up individual microbial cells or spores under the microscope with capillary or microneedles, hooks, rings, etc., so as to obtain pure culture. Single cell separation requires high technical requirements.
Culture
1. According to whether oxygen is needed during culture, it can be divided into aerobic culture and anaerobic culture.
Aerobic culture: This microbe requires oxygen to be added to the culture or it will not grow well. In the laboratory, bevel culture is provided with sterile air from the outside via cotton plugs. The liquid culture of the triangle flask is mostly vibrated by the shaker, so that the outside air keeps flowing into the flask.
Anaerobic culture: These organisms do not require oxygen in their culture. One of the most important aspects of anaerobic microbial culture is the removal of oxygen from the culture medium.
2. According to the physical state of the medium, it can be divided into two categories: solid culture and liquid culture.
Solid culture: a method of microbe culture by attaching a strain to a loose and nutrient-rich solid medium under suitable conditions.
Liquid culture: In the experiment, the liquid culture can make the rapid propagation of microorganisms, obtain a large number of culture, under certain conditions, or the effective method of microbial selection to increase bacteria.
Post time:2024-08-01